Tiny 'Hurricane-like' magnetic swirls could hold key to next AI breakthrough — material found in rust could help power energy efficient, brain-like processors capable of running at hundreds of Gigahertz
Researchers from Oxford University’s Department of Physics have made a discovery that could pave the way for the next big breakthrough in AI.
The team has successfully created 'hurricane-like' magnetic whirls in hematite, the main component of rust, which could potentially power energy-efficient, brain-like processors running at hundreds of Gigahertz.
These magnetic whirls, capable of moving at astonishing speeds of up to kilometers per second, are being touted as potential information carriers for the next generation of green and super-fast computing platforms.
100-1000 times faster
The study, published in Nature Materials, overcame the challenge of producing these whirls in materials that were previously incompatible with silicon, a major hurdle in their practical application.
The research was led by Dr. Hariom Jani from Oxford University, in collaboration with the National University of Singapore and the Swiss Light Source. Dr. Jani believes that silicon-based computing, with its high energy inefficiency, is not suitable for the next generation of computing applications such as full-scale AI and autonomous devices.
The solution, he suggests, lies in harnessing magnetic whirls in a special class of materials called antiferromagnets, which operate 100-1000 times faster than modern devices.
"Today, silicon transistors use charges to perform computation, which can dissipate as soon as electric supply is switched off. Hence, they tend to be very power hungry and inefficient. Moreover, conventional computers keep data-storage separate from data-processing. Shuttling information between them is time- and energy-intensive, creating a bottleneck in performance," Dr. Jani told us.
"On the other hand, hurricane-like whirls in antiferromagnetic materials are ‘protected’ nanoscale spin structures that are intrinsically stable thanks to their unique winding. They can remain stable even in the absence of electrical impulses. Moreover, they also host rich and ultra-fast dynamics which can be harnessed to perform unconventional information processing, where memory and logic functions can be married together. In the future, such platforms could be used to perform brain-like computing to make efficient and fast AI hardware."
The team achieved their breakthrough by fabricating ultra-thin crystalline membranes of hematite, on a crystal template coated with a special 'sacrificial layer'. The layer dissolved in water, separating the hematite from the crystal base, which was then transferred onto silicon and several other platforms.
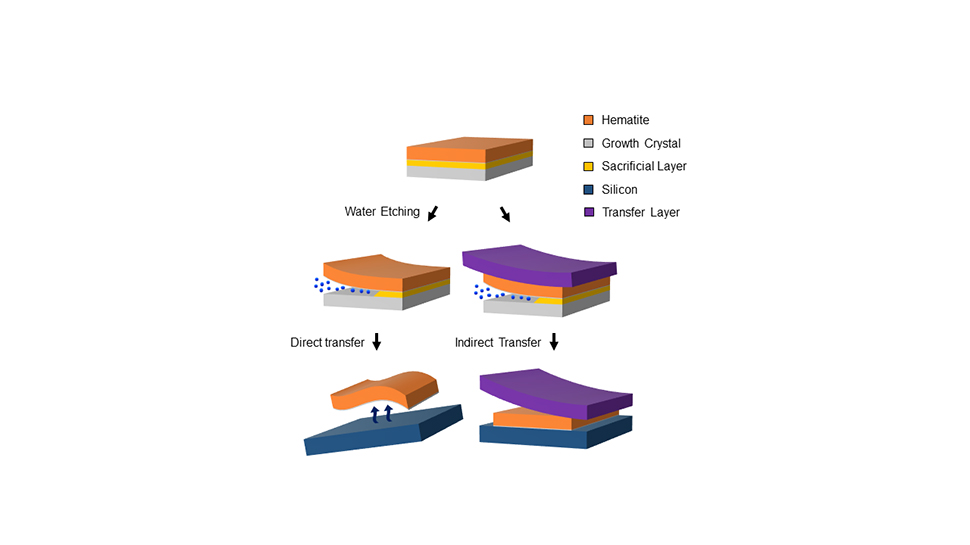
The researchers also developed a novel imaging technique using linearly polarized X-rays to visualize the nanoscale magnetic patterns within these membranes. The technique revealed that the free-standing layers can host a robust family of magnetic whirls, opening the door for ultra-fast information processing.
The team is now developing prototype devices to exploit the dynamics of these super-fast whirls. Dr. Jani concluded, "Eventually, such devices could be integrated into new types of computers that work more like the human brain – we are very excited about what’s coming next."
More from TechRadar Pro
- These are the fastest hard drives around today
- Anywhere there's a camera, now there's a risk say researchers
- Deepfake threats are on the rise
via Hosting & Support
Comments
Post a Comment